Completion requirements
View
2. What is an Operator?
2.4. Assignment Operators
There is a difference between using one equal sign (=), two equal signs (==) and three equal signs (===). The two and three equal signs are used to compare values and data types of two operands. One equal sign (=) is not used to compare values but rather assigns the value of the right operand to the left. For example, you can assign the value of y to x by simply writing x = y.
There are compound assignment operators that can be written in shorthand form. The table
below summarized the shorthand assignment operators.
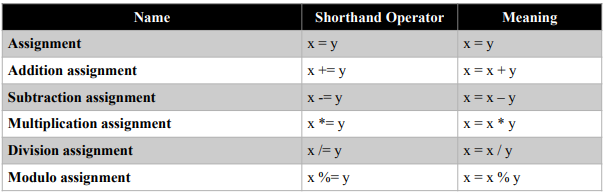
Sample Code:

Output:
