JavaScript Operations
| Site: | Philippine Science High School - MC - Knowledge Hub |
| Course: | SY25.CS3.Web Development |
| Book: | JavaScript Operations |
| Printed by: | , Guest user |
| Date: | Friday, 27 February 2026, 3:17 PM |
1. Introduction
After completing this module, you are expected to:
- Know the basic operations of JavaScript
- Manipulate and convert data using basic operations
Supposed, you are going to check whether a user input is greater than a default number. In order to do this, you should be able to compare the value of the user input and default number. The comparison of these two numbers will require you to use the JavaScript comparison operator.
In this module, you will be able to learn not only comparison operators but also other
operations you can use to manipulate data in JavaScript.
2. What is an Operator?
In the expression 7 + 3 = 10, 7 and 3 are operands and the '+' sign is the operator.
There are different types of operators that are being supported by JavaScript. These are the following operators:
- Arithmetic Operators
- Comparison Operators
- Logical Operators
- Assignment Operators
- Ternary Operators
2.1. Arithmetic Operators
Suppose you have variables a = 20 and b = 30. You can apply the following operations
- Addition (+): Adds two operands Ex. a + b will result to 50.
- Subtraction (-): Subtracts the second operand from the first Ex. a – b will result to -10.
- Multiplication (*): Multiply both operands Ex. a * b will result to 600.
- Division (/): Divide the numerator by the denominator Ex. b / a will result to 1.5.
- Modulus (%): Outputs the remainder of an integer division Ex. a % b will result to 20.
- Increment (++): Adds one to its operand. Ex. a++ will result to 21.
- Decrement (--): Subtracts the second operand from the first Ex. a-- will result to 19.
For incrementing and decrementing, if a prefix operator (++x or --x) is used, it will return the
value of the operand after adding one. Meanwhile, the postfix operator (x++ or x--) will return the
value of the operand before adding one. For example, if x = 5, then ++x sets x to 6 and returns 6,
while x++ returns 5 and, only then, sets x to 6.
Sample code:

Output:

2.2. Comparison Operators
To compare two values, you can use the JavaScript comparison operators. Supposed a = 20 and b = 30, let us try to compare the two values:
- Equal (==): It checks whether the two values are equal or not. If the two values are equal, then the condition is true. Ex. a == b is false.
- Not Equal (!=): It checks whether the two values are equal or not. If the two values are not equal, then the condition is true. Ex. a != b is true.
- Greater than (>): It checks whether the value on the left side is greater than the right. If yes, then the condition is true. Ex. a > b is false.
- Less than (<): It checks whether the value on the left side is less than the right. If yes, then the condition is true. Ex. a < b is true.
- Greater than or Equal to (>=): It checks whether the value on the left side is greater than or equal to the right. If yes, then the condition is true.
Ex. a >= b is false.
- Less than or Equal to (<=): It checks whether the value on the left side is less than or equal to the right. If yes, then the condition is true.
Ex. a <= b is true.
- Strictly Equal (===): It checks whether the two values are equal and of the same type. If yes, then the condition is true. Ex. a === "20" is false.
- Strictly Not Equal (!==): It checks whether the two values are not equal and not of the same type. If yes, then the condition is true. Ex. a !== "20" is true.
Take note that in strictly equal and strictly not equal operations, it does not only check whether the two values are equal but also if they are of the same type. In the example given, variable a is an integer type of data while "20" is a string. So, if we compare a === "20", the result is false. It is because even if both of them are of the same value (20), these two are not of the same type.
Sample Code:

Output:

2.3. Logical Operators
Logical operators are usually used with conditional operations and will return a Boolean value. However, if these operators are used with non-Boolean values, it may return a non-Boolean value.
- Logical AND (&&): For Boolean operands, it will return true if both operands are true; otherwise, it will return false. For non-Boolean operands, it will return the operand on the left if it can be converted to false; otherwise, it will return the operand on the right.
Ex. true && true will return true while "cat" && "dog" will return "dog".
- Logical OR (||): For Boolean operands, it will return false if both operands are false; otherwise, it will return true. For non-Boolean operands, it will return the operand on the left if it can be converted to true; otherwise, it will return the operand on the right.
Ex. false || false will return false while "cat" || "dog" will return "cat".
- Logical NOT(!): It returns true if the operand is evaluated to false; otherwise, returns false.
Ex. !(5=='5') will return false.

Output:

2.4. Assignment Operators
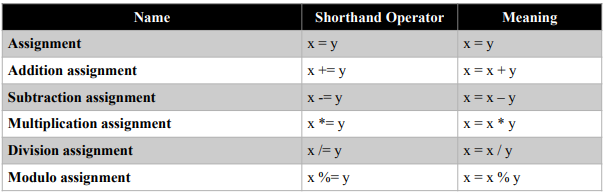
There is a difference between using one equal sign (=), two equal signs (==) and three equal signs (===). The two and three equal signs are used to compare values and data types of two operands. One equal sign (=) is not used to compare values but rather assigns the value of the right operand to the left. For example, you can assign the value of y to x by simply writing x = y.
There are compound assignment operators that can be written in shorthand form. The table
below summarized the shorthand assignment operators.
Sample Code:

Output:

3. Summary and References
In summary,
- JavaScript includes operators that perform some operation on single or multiple operands (data value) and produce a result.
- JavaScript includes various categories of operators: Arithmetic operators, Comparison operators, Logical operators, Assignment operators
References:
Expressions and operators. (n.d.). MDN Web Docs. Retrieved December 7, 2020, from https://developer.mozilla.org/en-US/docs/Web/JavaScript/Guide/Expressions_and_Operators
Javascript Operators. (n.d.). Retrieved December 7, 2020, from https://www.tutorialsteacher.com/javascript/javascript-operators
JavaScript—Operators—Tutorialspoint. (n.d.). Retrieved December 7, 2020, from https:// www.tutorialspoint.com/javascript/javascript_operators.htm