CSS Box Model
| Site: | Philippine Science High School - MC - Knowledge Hub |
| Course: | SY25.CS3.Web Development |
| Book: | CSS Box Model |
| Printed by: | , Guest user |
| Date: | Friday, 27 February 2026, 7:40 PM |
1. Introduction
After completing this module, you are expected to:
- Understand and use the CSS border, margin and padding properties
- Apply the CSS box model to webpages
In the previous module, you have learned some common properties in CSS which helps in the
design and layout of a webpage. The properties discussed include setting a background, background
images, color, font and text styles.
In this module, you will get to know how to add border, margin and padding. These properties are used to properly layout your HTML elements. To understand more about layout using CSS, the box model will be used.
The way our webpage content is displayed matters to readers or users of the page. Just like a word document, we can also set the border, margin and add padding to our web page. Using the box model below, it will guide you in organizing the way you display your page content.
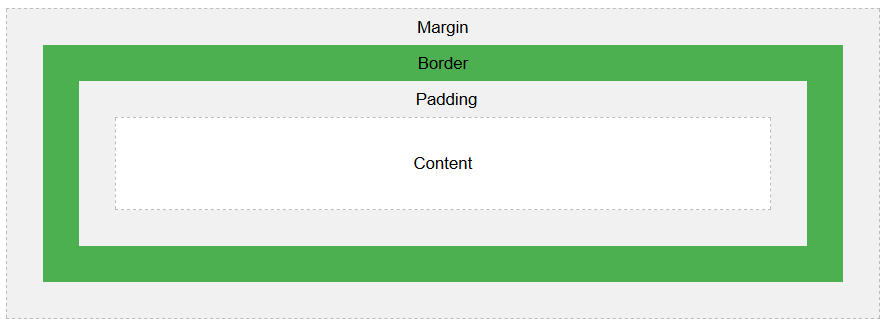
Source: https://www.w3schools.com/css/css_boxmodel.asp.
2. CSS Border
This property is used to specify how the border of the element should look. There are three properties of border which can be changed to achieve the desired layout/design (CSS - Borders - Tutorialspoint, n.d.).
border-color – it is used to specify the color of the border. It is also possible to change the individual color of the border (top, bottom, left and right). To do this, the property border-bottom-color, border-top-color, border-leftcolor and border-right-color are used.

border-style – the style of border can also be changed. Normally, the value solid is used since
it creates a single solid line border. But there are a lot of values that can be used for border-style. It could be none (no border), dotted (series of dots), dashed (series of short lines), double (two solid lines) and many more. Just like border-color,
it is also possible to change the style of each side of the border. For the different border styles, you may refer to Figure 1.


Figure 1. Different border styles applied in an element.
(Source: https://www.tutorialspoint.com/css/css_borders.htm)
border-width – it specifies the width of an element border. The value of this property can be set in using length (px, pt or cm) or set to thin, medium or thick. Each side of the border can also have different widths. If there is only one value for the width, it means all sides of the border will have that width value. However, if there will be two values, the first value corresponds to the top and bottom while the second value corresponds to the left and right. If 4 values are given, each value corresponds to top, right, bottom and left side of the border, respectively.
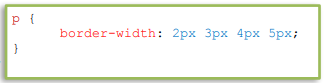
All the three properties can be merged into one shorthand property. Using the border property, you can set the width, style and color at the same time in this particular order.

3. CSS Margins
The margin property sets the space around an HTML element. This property can have a negative value which will result in overlapping of content. Margin will not be inherited by the child element. A shorthand property of margin can be used to set in one declaration the top, right, bottom and left margin, in this particular order. The auto value of this property will automatically set the margin left and right of the element equally.
- margin-top – sets the top margin of an element.
- margin-bottom – sets the bottom margin of an element.
- margin-left – sets the left margin of an element.
- margin-right – sets the right margin of an element.


 Note: You cannot set the top and bottom margin (also padding) in an inline element. Only the left and right can be set since the inline element flows with the content on the page.
Note: You cannot set the top and bottom margin (also padding) in an inline element. Only the left and right can be set since the inline element flows with the content on the page.
4. CSS Padding
The space between the content of the element and its border is the padding. The padding property will set how much this space should appear in the page. The shorthand property works the same as the shorthand property of margin. It is also possible to change the padding individually.
- padding-top – defines the top padding of an element. p
- adding-right – defines the right padding of an element.
- padding-bottom – defines the bottom padding of an element.
- padding-left – defines the left padding of an element.
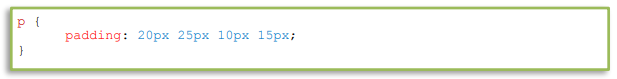
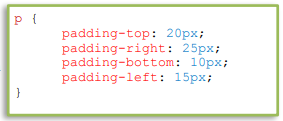
5. CSS Box Model
Every element in an HTML document is rendered by a web browser as a rectangular box based on the CSS box model. The CSS box model is a container that wraps around an HTML element. It contains the properties such as borders, margin, padding and the content of the element itself. This model is used to customize the layout of each element.
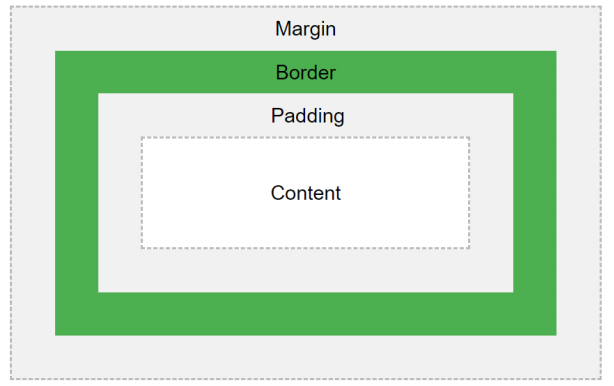
Figure 2. The box model containing margin, border, padding, content.
Source: https://www.w3schools.com/css/css_boxmodel.asp)
5.1. Listing 5.5.1
Let's look closely at this example on Listing 5.5.1. The element has a border of 15px,
padding of 50px and margin of 20px. Its result should look like in Figure 3. The entire element,
expanded in the entire web page with a margin of 20px on all sides. There is also 50px padding that
gives space between the border and content.
Listing 5.5.1 Box Border Example
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<style>
div {
background-color: lightgrey;
border: 15px solid green;
padding: 50px;
margin: 20px;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<h2>Demonstrating the Box Model</h2>
<div>This text is the content of the box. We have added a 50px padding,
20px margin and a 15px green border.
</div>
</body>
</html>

Figure 3. Output of Listing 5.5.1 Box Model Example
5.2. Listing 5.5.2
The size of the box can be specified using width and height properties. If the width of the element is set to 300px (see Listing 5.5.2), the content will then fit to a 300px width (see Figure 4). The height of the element is adjusted to fit the content. If the height is specified, there is a possibility that the content will overflow especially
when the content's height is greater than the specified height of the element. To resolve the problem of overflow, you may increase the height of the element or use the overflow property.
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<style>
div {
background-color: lightgrey;
width: 300px; /* change in width */
border: 15px solid green;
padding: 50px;
margin: 20px;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<h2>Demonstrating the Box Model</h2>
<div>This text is the content of the box. We have added a 50px padding,
20px margin and a 15px green border.
</div>
</body>
</html>
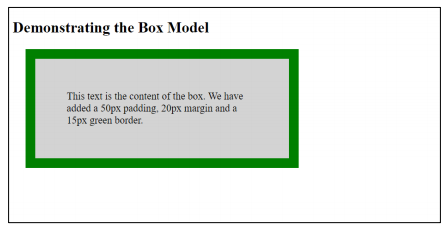
Figure 4. Output of Listing 5.5.2 with a width of 300px added to the element
The overflow property will set whether to add a scroll bar to the overflowed content or clip it.
The overflow property values include visible (default), hidden (clipped, and the rest is invisible),
scroll (clipped, and add scrollbar) and auto (add scroll only when necessary).
5.3. Listing 5.5.3
Remember that when you specify the width, by default, it sets the width of the content of the element not the element box. Thus, in Listing 5.5.2 the total width of the element is the sum of the left
and right border and padding and the width of the content which is 430px. This is because the box-sizing property of this element is set to content-box. But if the box-sizing property is set to border-box (see Listing 5.5.3), the sum of the left and
right border and padding and width of the content will be equal to 300px (see Figure 5). This is important especially in creating the layout of the web page. Basically, you might want to do this to all your HTML elements. Instead of adding the property
box-sizing in all the elements, you can use the universal selector and add the style rule for box-sizing.
Listing 5.5.3 Box Border Example with box-sizing set to border-box
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<style>
* {
box-sizing: border-box; /* inclusion of box-sizing */
}
div {
background-color: lightgrey;
width: 300px;
border: 15px solid green;
padding: 50px;
margin: 20px;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<h2>Demonstrating the Box Model</h2>
<div>This text is the content of the box. We have added a 50px padding,
20px margin and a 15px green border.
</div>
</body>
</html>
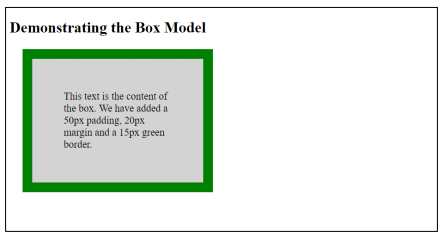
Figure 5. Output of Listing 5.5.3 when box-sizing is added
6. Summary
In summary, the CSS box model is important in the layout and design of an HTML webpage.
It consists of border, margin, padding and the content of the element. Setting these properties will
enhance the layout and design of the page. The box-sizing property can be set to either content-box or
border box. Content-box will set the width of the content of an element while the border-box will
consider the border, padding and the width of the content to set the width of the element box.
Width and height of the element can also be set using the width and height properties. When the height of the element is less than the height of its content, there is an overflow of the content. Resolving overflow will use the overflow property. With this, you can clip the overflowed element and either add a scroll to see the rest of the content or hide it.
References
CSS | Box model. (2018, August 16). GeeksforGeeks. https://www.geeksforgeeks.org/cssbox-model/
CSS - Borders—Tutorialspoint. (n.d.). Retrieved July 16, 2020, from https://
www.tutorialspoint.com/css/css_borders.htm
CSS - Margins—Tutorialspoint. (n.d.). Retrieved July 16, 2020, from https://
www.tutorialspoint.com/css/css_margins.htm
CSS - Paddings—Tutorialspoint. (n.d.). Retrieved July 16, 2020, from https://
www.tutorialspoint.com/css/css_padding.htm
CSS Box Model. (n.d.). Retrieved July 16, 2020, from https://www.w3schools.com/css/
css_boxmodel.asp